Understanding the past tense is essential for anyone learning English. It allows you to talk about actions or events that happened previously. Mastering this tense is crucial for effective communication, whether you’re telling a story, describing an experience, or discussing historical events.
In this guide, we will explore the different types of past tense in English, including their formation, usage, and examples. We will also address common mistakes and provide tips to help you use the past tense correctly and confidently.
By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the past tense in English, enabling you to use it accurately in both writing and conversation. Let’s delve into the nuances of the past tense and learn how to use it like a pro!
What is Past Tense?
The past tense in English grammar is used to describe actions, events, or conditions that occurred or were completed at a specific time in the past. This tense is vital for expressing what has already happened.
Types of Past Tense
1. Simple Past
The simple past tense is used to describe a completed action that happened at a specific time in the past.
- Usage: Used for actions completed in the past, often with time expressions like “yesterday,” “last year,” or “in 1990.”
- Formation: Add -ed to regular verbs or use the second form of irregular verbs.
- Examples:
- She walked to the store.
- They visited their grandparents last week.
- I watched a movie yesterday.
Note: The simple past tense is the most commonly used past tense in English and is straightforward to use.
2. Past Continuous
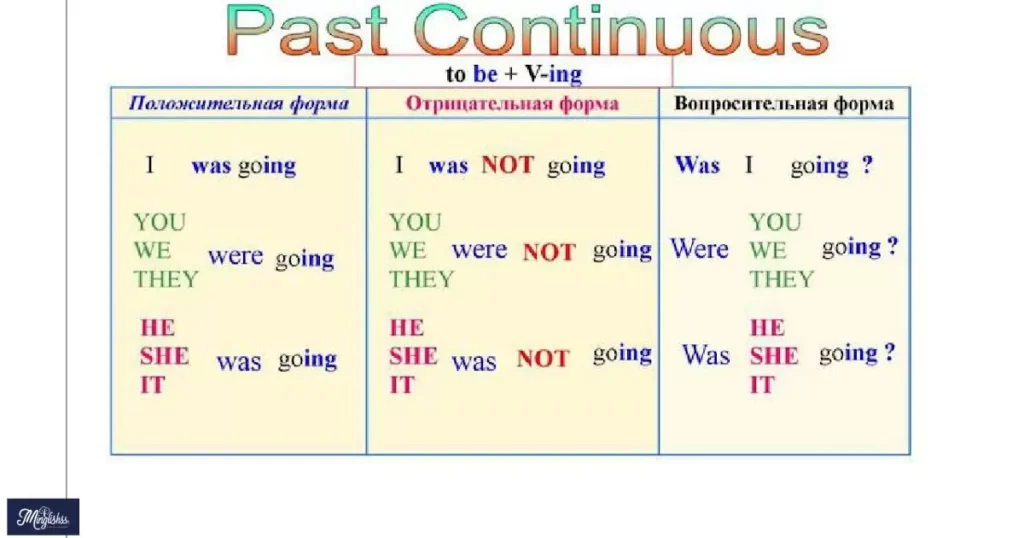
The past continuous tense describes an action that was ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Usage: Indicates an action that was in progress at a particular past moment.
- Formation: “was/were” + verb-ing.
- Examples:
- She was reading a book when I called.
- They were playing soccer at 4 PM yesterday.
- I was cooking dinner when the phone rang.
Note: The past continuous tense is useful for setting the scene in past narratives or describing simultaneous actions.
3. Past Perfect
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or time in the past.
- Usage: Expresses the idea that something occurred before another past event.
- Formation: “had” + past participle.
- Examples:
- She had left by the time I arrived.
- They had eaten dinner before the show started.
- I had finished the report before the deadline.
Note: The past perfect tense helps clarify the sequence of past events.
4. Past Perfect Continuous

The past perfect continuous tense describes an action that was ongoing before another action or time in the past.
- Usage: Emphasizes the duration of an action that continued up until a certain point in the past.
- Formation: “had been” + verb-ing.
- Examples:
- She had been studying for hours before the exam.
- They had been living there for five years before they moved.
- I had been working all day before I took a break.
Note: The past perfect continuous tense is ideal for highlighting the duration of an action in relation to another past event.
Uses of Past Tenses
Understanding when to use each type of past tense is key to conveying the correct meaning in your sentences. Here’s a quick overview:
1. Completed Actions in the Past
- Example: I visited my friend last week.
2. Actions in Progress at a Specific Past Time
- Example: She was watching TV at 8 PM last night.
3. Actions Completed Before Another Action
- Example: He had already left when I arrived.
4. Duration of Actions Leading Up to a Past Event
- Example: They had been waiting for hours before the train arrived.
WTV: What Does It Stand For and How Is It Used?
Sub-Categories of Sentences Using Past Tenses
Understanding how past tenses function in different sentence structures can improve clarity and fluency in your communication.
1. Declarative Sentences
- Usage: Make a statement about the past.
- Examples:
- She traveled to Japan last summer.
- They were eating dinner when I called.
- I had seen the movie before it was released.
- We had been waiting for the bus when it started raining.
- He played football in high school.
Note: Declarative sentences in past tense clearly state what happened.
2. Interrogative Sentences
- Usage: Ask a question about the past.
- Examples:
- Did she travel to Japan last summer?
- Were they eating dinner when you called?
- Had you seen the movie before it was released?
- Had they been waiting for the bus when it started raining?
- Did he play football in high school?
Note: Interrogative sentences in past tense often begin with “did,” “was/were,” or “had.”
3. Imperative Sentences
- Usage: While imperative sentences are primarily in the present, they can imply past actions through context.
- Examples:
- Think about what you did yesterday.
- Remember how you handled it last time.
- Review the steps you took earlier.
- Consider where you were last night.
- Reflect on your past decisions.
Note: Imperative sentences typically give commands or advice but can relate to past actions.
4. Conditional Sentences
- Usage: Express a condition and its past result.
- Examples:
- If she had studied, she would have passed the exam.
- If it had rained, we would have stayed indoors.
- If you had worked harder, you would have succeeded.
- If they had invited us, we would have gone.
- If I had finished early, I would have joined you.
Note: Conditional sentences in past tense often use “if” to connect the condition with its result.
5. Exclamatory Sentences
- Usage: Express strong emotion about a past event.
- Examples:
- What a great day it was!
- How amazing their performance was!
- I can’t believe we did it!
- What a surprise it was!
- How wonderful the trip had been!
Note: Exclamatory sentences in past tense emphasize strong emotions or reactions to past events.
Answers to Key Questions
Q1: What is the difference between the simple past and past perfect tense?
A1: The simple past describes a completed action at a specific time in the past, while the past perfect indicates an action completed before another past event.
Q2: When should I use the past continuous tense?
A2: Use the past continuous tense to describe an action that was in progress at a specific time in the past. For example, “She was reading when I arrived.”
Q3: Can the past perfect continuous tense be used for short actions?
A3: The past perfect continuous tense is typically used for actions that continued over a period of time before another event. It’s not usually used for short actions.
Q4: How do I form a negative sentence in the past simple tense?
A4: To form a negative sentence in the past simple tense, use “did not” (or “didn’t”) + the base form of the verb. For example, “She did not go to the party.”
Q5: What is an example of a past perfect tense sentence?
A5: An example is “By the time he arrived, we had already left.” This shows that the leaving occurred before the arriving.
Conclusion
Mastering the past tense is crucial for expressing what has already happened clearly and effectively. By understanding the various forms of the past tense and their appropriate uses, you can confidently talk about past events, describe experiences, and share stories.
Keep practicing, and soon using the past tense will become second nature!

I’m Jane Austen, a language expert at Minglishs, dedicated to helping learners master English through engaging and accessible content. My passion for literature and teaching drives me to make language learning both enjoyable and effective.










