Future tense plays a vital role in English grammar, allowing us to express actions or events that will happen later. Understanding how to use future tenses accurately is essential for clear communication, especially when making plans, predictions, or expressing intentions.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the different types of future tenses in English, including their formation, usage, and examples. Whether you’re just starting out with English or need a refresher, this comprehensive overview will help you master the future tense. We’ll also explore common mistakes to avoid and provide tips for using future tenses effectively.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid understanding of the future tense in English and how to use it correctly in your writing and speech. Let’s begin our journey into the future!
What is Future Tense?
Future tense in English grammar is used to describe actions or events that will happen at a later time. Unlike the present and past tenses, which refer to actions happening now or before, the future tense is all about what is yet to come.
Types of Future Tenses
1. Future Simple
The future simple tense is used to describe actions that will occur in the future without specifying a particular time.
- Usage: Expresses predictions, spontaneous decisions, or planned actions.
- Formation: “will” + base form of the verb.
- Examples:
- She will travel to Paris next month.
- I will call you later.
- They will win the game.
Note: The future simple tense is straightforward and often used for making promises or offers.
2. Future Continuous
The future continuous tense describes actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
- Usage: Indicates an action that will be in progress at a particular future moment.
- Formation: “will be” + verb-ing.
- Examples:
- She will be studying at 8 PM.
- They will be playing soccer tomorrow afternoon.
- I will be waiting for you at the station.
Note: The future continuous tense is useful for setting the scene in the future or discussing overlapping actions.
3. Future Perfect
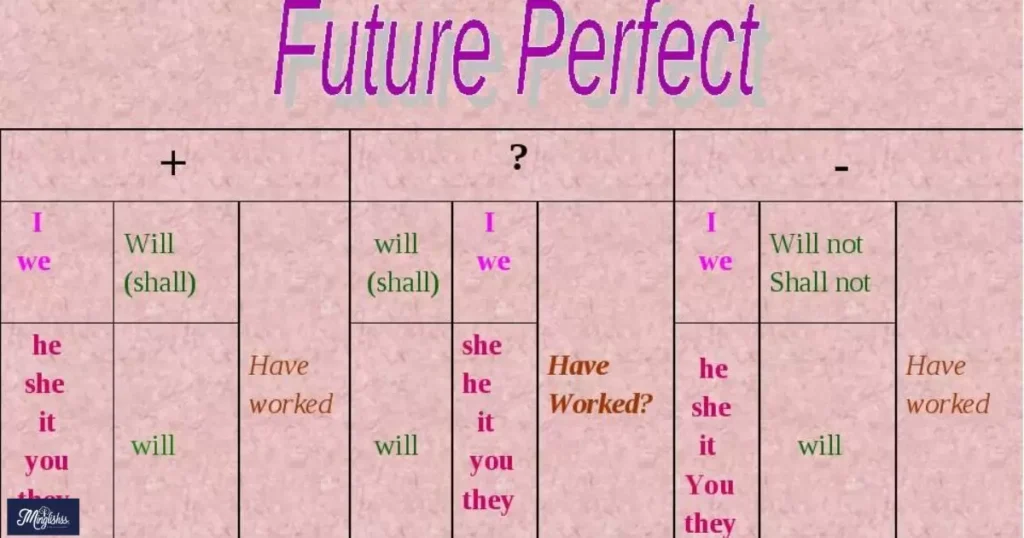
The future perfect tense is used to describe actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
- Usage: Expresses actions that will be finished by a certain future point.
- Formation: “will have” + past participle.
- Examples:
- She will have finished the project by tomorrow.
- They will have left before you arrive.
- I will have completed my degree by next year.
Note: The future perfect tense helps clarify the sequence of events in the future.
4. Future Perfect Continuous
The future perfect continuous tense describes actions that will have been ongoing up until a specific time in the future.
- Usage: Emphasizes the duration of an action that will be ongoing up to a future moment.
- Formation: “will have been” + verb-ing.
- Examples:
- She will have been studying for three hours by the time you arrive.
- They will have been living here for five years by next month.
- I will have been working on this project all day.
Note: The future perfect continuous tense is ideal for highlighting the duration of an action leading up to a future event.
Uses of Future Tenses
Understanding when to use each type of future tense is crucial for expressing the correct meaning in your sentences. Here’s a quick overview:
1. Predictions
- Example: It will rain tomorrow.
2. Spontaneous Decisions
- Example: I’ll help you with that.
3. Scheduled Actions
- Example: The train will leave at 9 PM.
4. Future Plans or Intentions
- Example: We are going to visit our grandparents this weekend.
5. Ongoing Actions at a Specific Future Time
- Example: She will be working at the office tomorrow.
6. Actions Completed Before a Future Event
- Example: They will have finished the task by then.
Abbreviations for ‘Director’: Essential Terms in Professional Settings
Sub-Categories of Sentences Using Future Tenses
Understanding sentence structures using future tenses can help in better sentence formation and clarity.
1. Declarative Sentences
- Usage: Make a statement about the future.
- Examples:
- She will travel to New York.
- They will be watching a movie tonight.
- I will have completed the report by tomorrow.
- We will be celebrating her birthday next week.
- He will have been working there for ten years by next month.
Note: Declarative sentences in future tense clearly state what is expected to happen.
2. Interrogative Sentences
- Usage: Ask a question about the future.
- Examples:
- Will she travel to New York?
- Will they be watching a movie tonight?
- Will you have completed the report by tomorrow?
- Will we be celebrating her birthday next week?
- Will he have been working there for ten years by next month?
Note: Interrogative sentences in future tense often begin with “will” followed by the subject.
3. Imperative Sentences
- Usage: Give a command or make a request related to the future.
- Examples:
- Please call me when you arrive.
- Finish this report by tomorrow.
- Be on time for the meeting.
- Don’t forget to submit your assignment.
- Let me know if you need any help.
Note: Imperative sentences in future tense often imply that the action should take place in the future.
4. Conditional Sentences
- Usage: Express a condition and its future result.
- Examples:
- If she studies, she will pass the exam.
- If it rains, we will stay indoors.
- If you work hard, you will succeed.
- If they invite us, we will go.
- If I finish early, I will join you.
Note: Conditional sentences in future tense often use “if” to connect the condition with its result.
5. Exclamatory Sentences
- Usage: Express strong emotion about a future event.
- Examples:
- What a beautiful day it will be!
- How exciting the trip will be!
- I can’t believe we’ll be graduating soon!
- What a great time we will have!
- How amazing the concert will be!
Note: Exclamatory sentences in future tense emphasize strong emotions or expectations.
Answers to Key Questions
Q1: How is the future perfect continuous tense different from the future continuous tense?
A1: The future continuous tense describes actions that will be ongoing at a specific future time, while the future perfect continuous emphasizes the duration of an action that will continue up to a specific future moment.
Q2: When should I use the future simple tense?
A2: Use the future simple tense for making predictions, spontaneous decisions, or stating future facts. For example, “It will rain tomorrow.”
Q3: Can I use “going to” instead of “will” for future actions?
A3: Yes, “going to” is often used for planned actions or when there is evidence that something will happen. For example, “I’m going to study tonight.”
Q4: What is an example of a future perfect tense sentence?
A4: An example is “By next week, I will have completed the project.” It shows that the action will be finished before a specific future time.
Q5: How do I form a future continuous tense sentence?
A5: Form the future continuous tense by using “will be” followed by the verb-ing form, such as “She will be studying at 8 PM.”
Conclusion
Mastering the future tense in English grammar is crucial for clear and accurate communication. By understanding and practicing the different types of future tenses, you can confidently express your intentions, plans, and predictions in both writing and speech.
Keep practicing, and soon using future tenses will become second nature!

Hi, I’m Zadie Smith: I’m dedicated to helping others master English through practical tips. I enjoy making complex ideas simple and accessible for everyone.










